Oral Health Conditions
- Sep 30, 2024
- 1 min read
A guide on common oral diseases and how they affect you.
Common Oral Diseases

Tooth Decay
Tooth Decay is the destruction of tooth structure by acids that are produced when bacteria breaks down foods.
If the decay progresses, bacteria may reach the root canal system and cause root canal infections.
While not all tooth decay causes pain, severe decay may lead to tooth loss.
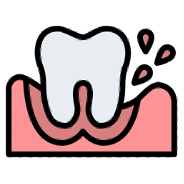
Gum disease
Gum Disease is the inflammation of the gums, bone and supporting structures of the teeth.
Symptoms include red and swollen gums, gums that bleed spontaneously or on brushing, painful gums, gum recession and persistent bad breath.
Severe gum disease may lead to shaky teeth and tooth loss
Root Canal Infections
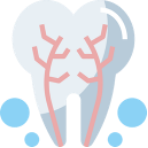
Root canal infections are infections of the root canal system, which is the soft tissue within each tooth that includes blood vessels and nerves.
Root canal infections can cause severe toothaches.
Common systemic diseases/factors that affect oral health
Diabetes
Diabetes is a known risk factor for gum disease, alsoworsening its progression and severity. Impaired healing response, altered microbial flora and vascular changes result in diabetics being 2 to 3 times as likely to develop severe gum disease than non-diabetics.
Smoking

Smoking is another known risk factor for gum disease, due to possible changes in the microbial flora of the oral cavity and altered immune response. Smokers more commonly suffer from increased bone loss and more rapid progression of gum disease.
Drugs that reduce saliva flow

The consumption of certain drug types may cause decrease in saliva flow - commonly in older patients on multiple medications. As saliva has important protective functions, reduced saliva flow increases the risk of developing tooth decay or oral infections. Some of these drugs include certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, diuretics, antihypertensive, anxiolytic and sedative drugs, NSAIDs, antihistamines, and opioid analgesics.
Written by: Kelsey Lim | Designed by: Chia Miao Ting | Edited by: Jonathan Kuek




Comments